


fecha:15 de mayo 2018
Practica caso 5: EN C++
tema:Estructoras seleccion multiple
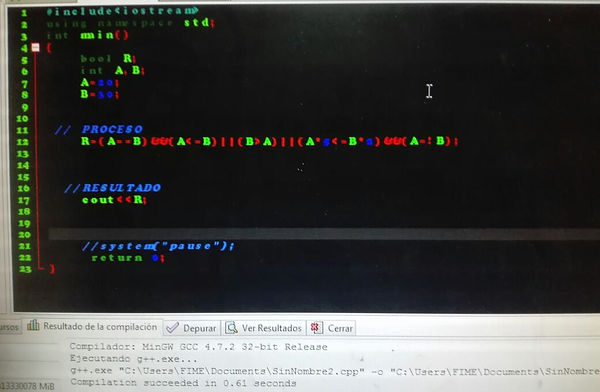
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int OPCION;
cout<<"menu polares";
cout<<"1.-suma \n";
cout<<"2.-resta \n";
cout<<"3.-multiplica \n";
cout<<"4.-dividir \n";
cout<<"ingrese una opcion";
cin<<opcion;
switch ( opcion )
{
CASE 1:{
{
int r1,r2,t1,t2;
double x1,x2,y1,y2,pi=3.14;
double b1,b2;
cout<<"Ingrese R1: "; cin>>r1;
cout<<"Ingrese t1: ";cin>>t1;
cout<<"Ingrese R2: ";cin>>r2;
cout<<"Ingrese t2: ";cin>>t2;
b1=((2*pi*t1)/360);
b2=((2*pi*t2)/360);
x1=r1*cos(b1);
x2=r2*cos(b2);
y2=r1*sin(b1);
y2=r1*sin(b2);
cout<<"z= "<<x1+x2<<"+j"<<y1+y2<<endl;
break;
}
CASE 2:{
int r1,r2,t1,t2;
double x1,x2,y1,y2,pi=3.14;
double b1,b2;
cout<<"Ingrese R1: ";cin>>r1;
cout<<"Ingrese t1: ";cin>>t1;
cout<<"Ingrese R2: ";cin>>r2;
cout<<"Ingrese t2: ";cin>>t2;
b1=((2*pi*t1)/360);
b2=((2*pi*t2)/360);
x1=r1*cos(b1);
x2=r2*cos(b2);
y2=r1*sin(b1);
y2=r1*sin(b2);
cout<<"z= "<<x1-x2<<"-j"<<y1-y2<<endl;
break;
}
CASE 3:{
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
double r1,r2,t1,t2;
cout<<"Ingrese x1: ";cin>>x1;
cout<<"Ingrese y1: ";cin>>y1;
cout<<"Ingrese x2: ";cin>>x2;
cout<<"Ingrese y2: ";cin>>y2;
r1=sqrt(pow(x1,2)+pow(y1,2));
r2=sqrt(pow(x2,2)+pow(y2,2));
t1=atan(y1/x1);
t2=atan(y2/x2);
x1=r1*cos(t1);
x2=r2*cos(t2);
y2=r1*sin(t1);
y2=r1*sin(t2);
cout<<"radio "<<r1*r2<<"*angulo: j"<<y1+y2<<endl;
break;
}
CASE 4:{
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
double r1,r2,t1,t2;
cout<<"Ingrese x1: ";cin>>x1;
cout<<"Ingrese y1: ";cin>>y1;
cout<<"Ingrese x2: ";cin>>x2;
cout<<"Ingrese y2: ";cin>>y2;
r1=sqrt(pow(x1,2)+pow(y1,2));
r2=sqrt(pow(x2,2)+pow(y2,2));
t1=atan(y1/x1);
t2=atan(y2/x2);
x1=r1*cos(t1);
x2=r2*cos(t2);
y2=r1*sin(t1);
y2=r1*sin(t2);
cout<<"radio "<<r1/r2<<"/angulo: "<<y1-y2<<endl;
break;
}
CASE 5:{
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
double r1,r2,t1,t2,s1,s2,pi=3.14;
double r,s,x,y;
cin>>x1;
cin>>y1;
cin>>x2;
cin>>y2;
r1=sqrt(pow(x1,2)+pow(y1,2));
r2=sqrt(pow(x1,2)+pow(y1,2));
t1=atan(y1/x1);
t2=atan(y2/x2);
s1=(r1*360)/(2*pi);
s2=(r2*360)/(2*pi);
r=r1*r2;
s=s1*s2;
x=r*cos(5);
y=r*sin(5);
cout<<"z= "<<x<<"+j"<<y<<endl;
break;



Estructoras condicionales

ESTRUCTORAS DE REPITICION

Encabezado 1
13 de JUNIO 2018
secion 09
estructora de repiticion ( por FOR)
EN WORD
13 DE JUNIO 2018
secion 09 for
ESTRUCTURA DE REPITICION INFINITA(POR FOR
D#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
cout<<"escoger una opcion\n ";
int opcion;
cout<<"1.-SUMATORIA \n";
cout<<"2.-TABLA DE MULTIPLICAR \n";
cout<<"3.-GASES IDEALES \n";
cout<<"4.-FUNCIONES \n";
cout<<"5.-FRECUENCIA ANGULAR \n";
cout<<"ingrese una opcion";
cin>>opcion;
switch ( opcion )
{
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
case 1:{
double n,j1,j2,j3,m,M;
cout<<"Numero max, contara uno en uno, empezando desde 1\n";cin>>M;
for (n=1;n<=M;n++)
{
j1=j1*n;
j2=j2*(n*2);
j3=j3*(2*n-1);
m=m*n;
cout<<"la sumatoria es : "<<j1<<endl;
cout<<"la sumatoria de j2 pares es: "<<j2<<endl;
cout<<"la sumatoria de j3 impares es: "<<j3<<endl;
cout<<"el factorial es: "<<m<<endl;
}
}
break;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
case 2:{
double i,j,min,max;
cin>>min;
cin>>max;
for (i=min;i<=max;i=i++)
for (j=min;j<=max;j=j++)
{
cout<< i <<"*"<< j <<"="= i*j;<<endl;
}
}
break;
case 3:{
double p1,,p2,t1,t2,v1,v2;
cout<<"tiempo 1"; cin>>t1;
cout<<"tiempo 2"; cin>>t2;
cout<<"ingresar p2"; cin>>p2;
for (v1=12;v1<=40;v1=v1++)
for (v2=20;v2<=35;v2=v2+3)
{
p1=(p2*v2*t1)/v1*t2;
cout<<p1<<endl;
}
}
break;
case 4:{
int x,min,max,p;
double f,pi=3.14;
cin>>min;
cin>>max;
for(x=min;x<=max;x=+4)
{
p=(2*pi*x)/360;
f=(cosh(p))-(sin(p));
cout<<f<<endl;
}
}
break;
case 5:{
double a,t,wf,wi;
cout<<"tiempo: ";cin>>t;
for (wf=20;wf<=50;wf=wf+5)
for (wi=10;wi<=50;wi=wi+10)
{
a=(wf-wi)/t;
cout<<"l aceleracion angular es: "<<a<<endl;
}
}
break;
}
}
19 DE JUNIO 2018
C++ FUNCIONES
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
double Fx,R,Q;
double x,a,n,B,P,i;
double r,xl,xc,I,V;
double p,v,pi=3.14,m,G;
double PARABOLA(int a);
double RAIZ (int x,int y);
double CORRIENTE(int ñ,int l ,int u,int z)
double POTENCIA(int A,int b,int c)
int opcion;
int main ()
{
cout<<"MENU\n";
cout<<"PARABOLA:\n";
cout<<"PARABOLA 2:\n";
cout<<"RAIZ:\n";
cout<<"CORRIENTE:\n";
cout<<"CORRIENTE 2:\n";
cout<<"POTENCIA:\n";
cout<<"POTENCIA 2:\n";
cout<<"ingrese una opcion: ";
cin>> opcion;
switch(opcion)
{
case 1:
{
cout<<"PARABOLA\n";
Q= PARABOLA(x);
cout <<"para x: "<<x<<" el valor de f(x)= "<< r <<endl;
};break;
case 2:
{
for(x=-5;x<=5;x++)
{
R= PARABOLA(x);
cout <<"para x: "<<x<<" el valor de f(x)= "<< x <<endl;
}
};break;
case 3:
{
cout<<"RAIZ\n";
a=1;
cin>>n;
cin>>B;
do
{
R=RAIZ(a,B);
cout<<R<<endl;
a=a++;
} while(a<=n);
};break;
case 4:
{
cout<<"CORRIENTE\n";
cout<<"Ingrese el Voltaje: "; cin>>V;
cout<<"Ingrese resistencia:"; cin>>r;
cout<<"Ingrese xl: "; cin>>xl;
cout<<"Ingrese xc: "; cin>>xc;
I=CORRIENTE(V,r,xl,xc);
cout<<I<<endl;
}
;break;
case 5:
{
cout<<"Ingrese xl:"; cin>>xl;
cout<<"Ingrese xc:"; cin>>xc;
for(V=8; V<=30; V=V+1)
for(r=10;r<=20; r=r+4)
{
I=CORRIENTE(V,r,xl,xc);
cout<<I<<endl;
}
}
;break;
case 6:
{
cout<<"POTENCIA\n";
cout<<"Ingrese el angulo: ";cin>>m;
cout<<"Ingrese voltaje : ";cin>>v;
cout<<"Ingrese intensidad: ";cin>>i;
P=POTENCIA(v,i,m);
cout<<P<<endl;
}
;break;
case 7:
{
cout<<"Ingrese el angulo: ";cin>>m;
for(v=1; v<=10; v=v++)
for(i=7; i<=25; i=i++)
{
P=POTENCIA(v,i,m);
cout<<P<<endl;
}
};break;
}
}
double PARABOLA(int a)
{
Q=(1/pow(a,2))+3;
return Q ;
}
double RAIZ (int x,int y)
{
Q=pow(x,1/y);
return Q;
}
double CORRIENTE(int ñ,int l ,int u,int z)
{
I=ñ/(sqrt(pow(l,2)+(u+z,2)));
return I;
}
double POTENCIA(int A,int b,int c)
{
G=(2*pi*c/360);
P=A*b*(cos(G));
return P;
}
04 de julio del 2018
secion 13
vectores
ARREGLOS UNIDIMENSIONALES
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
int opcion,i,suma,prom,mayor,indice;
int leer_vector();
int v[10],sumar_vector();
int respuesta_prom_vector();
int a[10],b[10],c[10];
int vectores();
int sumar ();
int promedio();
int valor_maxi();
int valor_mini();
int main ()
{
do
{
cout<<"MENU\n";
cout<<"1.leer vector\n";
cout<<"2.suam de vector\n";
cout<<"3.respuesta de vector\n";
cout<<"4.dos vectores\n";
cout<<"5. la suma es\n";
cout<<"6. el promedio es\n";
cout<<"7.el valor max\n";
cout<<"8.el valor minimo\n";
cout<<"ingrese una opción:";
cin>>opcion;
switch(opcion)
{
case 1:
{
leer_vector();
};break;
case 2:
{
sumar_vector();
};break;
case 3:
{
respuesta_prom_vector();
};break;
case 4:
{
vectores ();
};break;
case 5:
{
sumar();
};break;
case 6:
{
promedio():
} ;break;
case 7:
{
valor_maxi();
}
case 8;
{
valor_mini();
}
}//Fin switch
} while (opcion= !0);
//system "pause"()
return 0 ;
}
//ZONA DE FUNCIONES XD
int leer_vector()
{
for (i=1;i<=10;i++)
cin>> v[i];
}
int sumar_vector()
{
suma=0;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
suma =suma+v[i];
cout<<" la suma en el vetor sera:"<<suma<<endl;
}
int respuesta_prom_vector()
{
prom=suma/10;
cout<<"el promedio sera:"<<prom<<endl;
}
int vectores()
{
cout<<"ingrese elementos para el vector a:";
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
cin>> a[i];
cout<<"ingrese elementos para el vector b:";
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
cin>>b[i];
}
int sumar()
{
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
c[i]=a[i]+b[i];
}
int promedio()
{
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
suma=suma+c[i];
promedio=suma/10;
}
int valor_maxi()
{
maxi=c[1];
for(i=1,i<=10;i++)
{
if(c[i]>=maxi)
{
maxi=c[i];
indice=i;
}
}
cout<< "el valor maximo es:"<<maxi<<endl;
cout<<"el valor del indice es:"<<indice<<endl;
}
int valor_mini()
{
mini=c[1];
for(i=1,i<=10;i++)
{
if(c[i]>=min)
{
min=c[i];
indice=i;
}
}
cout<<"el valor minimo sera:"<<mini<<endl;
cout<<"el indice sera:"<<indice<<endl;
}
}

VIDEO DE MATRICES C++
TEMA : MATRICESS CC++
10 de JULIO DEL 2018
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace std ;
int opcion;
int V[20];
int M[3][3];
int i,j;
int A[3][3],B[3][3],C[3][3];
int indicA;
int indicB;
int multi;
int suma,promedio;
int maxi,mini;
int leer_2_matrices();
int ver_suma_2_matrices();
int promedio_matriz();
int mayor_y_sus_indices();
int menor_y_sus_indices();
int transpuesta();
int indice_matriz();
int main ()
{ do{
cout<<"*******MENU*******\n";
cout<<"leer_2_matrices :\n";
cout<<"ver_suma_2_matrices :\n";
cout<<"promedio_matriz:\n";
cout<<"mayor_y_sus_indices:\n";
cout<<"menor_y_sus_indices:\n";
cout<<"transpuesta:\n";
cout<<"indice:\n";
cout<<"ingrese una opcion: ";
cin>> opcion;
switch(opcion)
{
case 1:
{
leer_2_matrices();
};break;
case 2:
{
ver_suma_2_matrices();
};break;
case 3:
{
promedio_matriz();
};break;
case 4:
{
mayor_y_sus_indices();
};break;
case 5:
{
menor_y_sus_indices();
};break;
case 6:
{
transpuesta();
};break;
case 7:
{
indice_matriz();
};break;
}
}while(opcion=!0);
return 0 ;
}
int leer_2_matrices()
{
for (i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
cout<< "A["<<i<<"]["<<j<<"]= "; cin>> A[i][j];
}
}
for (i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
cout<< "B["<<i<<"]["<<j<<"]= "; cin>> B[i][j];
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
int ver_suma_2_matrices()
{
for (i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
M[i][j]= A[i][j]+B[i][j];
cout <<"["<<i<<"]"<<"["<<j<<"]:"<<M[i][j]<<endl;
}
}
}
int promedio_matriz()
{
suma=0;
for(i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=3;j++)
suma=suma+M[i][j];
{
promedio=suma/(i*j);
}
}cout<<promedio<<endl;
}
int mayor_y_sus_indices()
{
maxi=M[1][1];
for (i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
if (M[i][j]>maxi)
{
maxi=M[i][j];
indicA= i;
indicB= j;
}
}
}
cout<< indicA<<endl;
cout<< indicB<<endl;
cout<<"matriz MAXIMA :"<<maxi<<endl;
}
int menor_y_sus_indices()
{
mini=M[1][1];
for (i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
if (M[i][j]<mini)
{
mini=M[i][j];
indicA= i;
indicB= j;
}
}
}
cout<< indicA<<endl;
cout<< indicB<<endl;
cout<<"matriz MINIMA :"<<mini<<endl;
}
int transpuesta()
{
for (i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
for (j=1;j<=3;j++)
{
cout<< "M["<<j<<"]["<<i<<"]= "<< M[j][i]<<endl;
}
}
}
10 DE JULIO 2018 MATRICES CC++ EN WORD
19 DE JUNIO 2018
C++ FUNCIONES EN WORD
FECHA 15 DE MAYO 2018
Practica caso 5: EN C++
tema:Estructoras seleccion multiple
fecha:15 de mayo 2018
PRESENTADO EN IMAGENES
Encabezado 5
Soy un párrafo. Haz clic aquí para agregar tu propio texto y edítame. Es muy sencillo.











